CNC machining is a term commonly used in manufacturing and industrial applications. But what exactly is CNC? What is a CNC machine tool?

CNC machine tools for milling workpieces.
CNC 101: The term CNC stands for "Computer Numerical Control" and CNC machining is defined as a subtractive manufacturing process that typically employs computer controls and machine tools from stock parts (called blanks or workpieces) and produces custom-designed parts. The process is suitable for a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, wood, glass, foams and composites, and is used in a variety of industries such as large CNC machining, machining of telecom parts and prototypes, and CNC machining of aerospace parts. Tighter tolerances are required than in other industries. Note that there is a difference between a CNC machining definition and a CNC machine definition - one is a process and the other is a machine. A CNC machine (sometimes incorrectly referred to as a C and C machine) is a A programmable machine tool capable of autonomously performing CNC machining operations.
CNC machining is available worldwide as a manufacturing process and service. You can easily find CNC machining services in Europe, Asia, North America and the rest of the world.
Subtractive manufacturing processes (such as CNC machining) are often contrasted with additive manufacturing processes (such as 3D printing) or forming manufacturing processes (such as liquid injection molding). Subtractive processes remove layers of material from a workpiece to produce custom shapes and designs, Whereas additive processes assemble layers of material to produce the desired shape, molding processes deform and displace the raw material into the desired shape. The automated nature of CNC machining enables the production of high-precision, high-precision, simple parts and cost-effectiveness while completing one-off and medium-volume production runs. However, while CNC machining has shown some advantages over other manufacturing processes, there are limits to the level of sophistication that can be achieved in part design and the cost-effectiveness of producing complex parts.
While each manufacturing process has its advantages and disadvantages, this article focuses on the CNC machining process, outlining the basics of the process, as well as the various components and tools of CNC machine tools. Furthermore, this paper explores various mechanical CNC machining operations and proposes alternatives to the CNC machining process.
At a glance, this guide will cover:
Overview of CNC machining process
Types of CNC Machining Operations
CNC machining equipment and components
CNC machining materials
CNC Dimension Notes
Alternatives to using CNC machines
CNC machining history
Are you currently between jobs or an employer looking to recruit? We provide an in-depth collection of resources for industrial job seekers and employers looking to fill vacancies. If you have a job opening, you can also fill out our form for a chance to be featured in the Thomas Monthly Update newsletter.
Overview of CNC machining process
Evolving from the numerically controlled (NC) machining process using punched tape cards, CNC machining is a manufacturing process that utilizes computer control to operate and manipulate machines and cutting tools to shape raw materials such as metal, plastic, wood, foam, composite Materials and more - custom parts and designs. While the CNC machining process offers a variety of functions and operations, the basic principles of the process are basically the same in all of them. The basic CNC machining process consists of the following stages:
Design CAD models
Convert CAD files to CNC programs
Preparing the CNC Machine
Perform machining operations
CAD model design
The CNC machining process begins with the creation of a 2D vector or 3D solid part CAD design in-house or at a CAD/CAM design service. Computer-aided design (CAD) software allows designers and manufacturers to make models or renderings of their parts and products, as well as the technical specifications, such as size and geometry, required to produce the parts or products.
The design of CNC machined parts is limited by the capabilities (or incapacities) of CNC machines and tools. For example, most CNC machines are cylindrical, so the part geometries that can be produced through the CNC machining process are limited because the tool creates curved corner sections. Additionally, the properties of the material being machined, tool design, and the machine's workholding capabilities further limit design possibilities, such as minimum part thickness, maximum part size, and inclusion and complexity of cavities and features.
Once the CAD design is complete, the designer exports it to a CNC-compatible file format such as STEP or IGES.
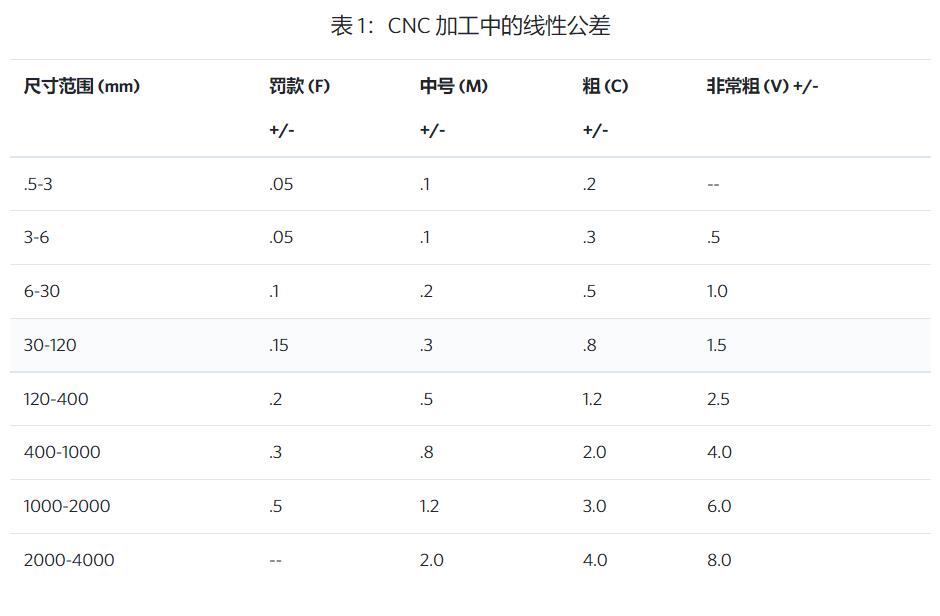
CNC machining tolerance table
When specifying parts to a machine shop, it is important to include any necessary tolerances. Although CNC machines are very precise, they still leave some slight differences between replicas of the same part, usually around + or - 0.005 inches (0.127 mm), which is about twice the width of a human hair. To save costs, buyers should only specify tolerances for areas of parts that need to be particularly accurate because they will come into contact with other parts. While there are standard tolerances for different machining levels (as shown in the table below), not all tolerances are created equal. For example, if a part can never be larger than the measured value, it might have a specified tolerance of +0.0/-0.5 to indicate that it can be slightly smaller, but not larger in that area.